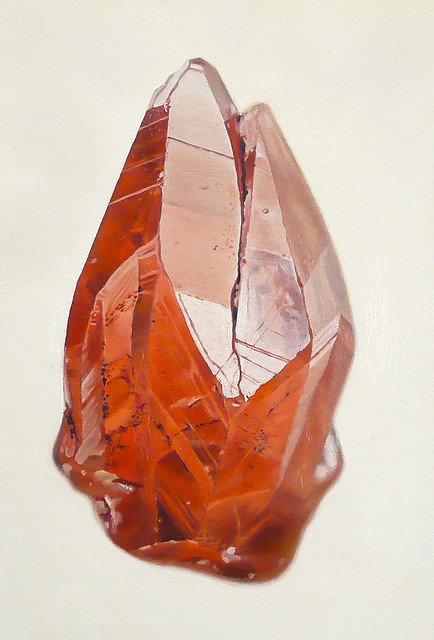
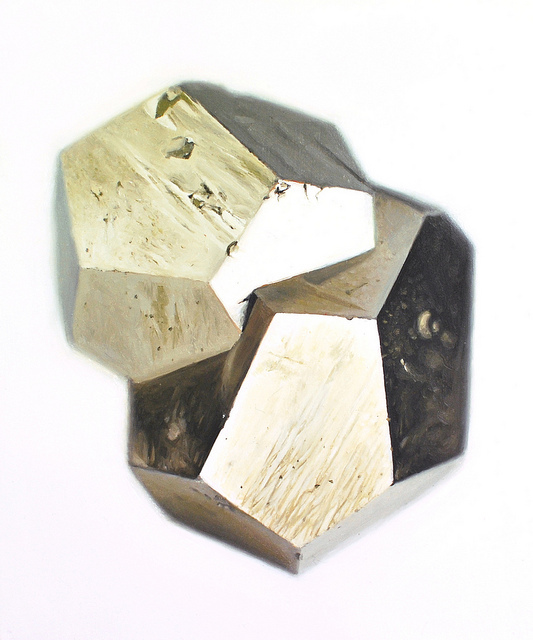
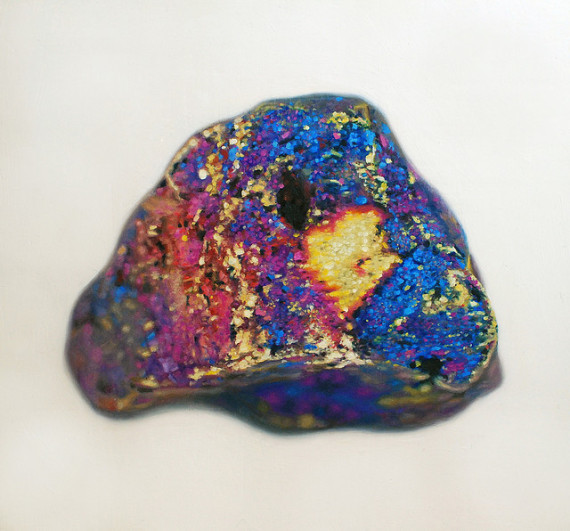
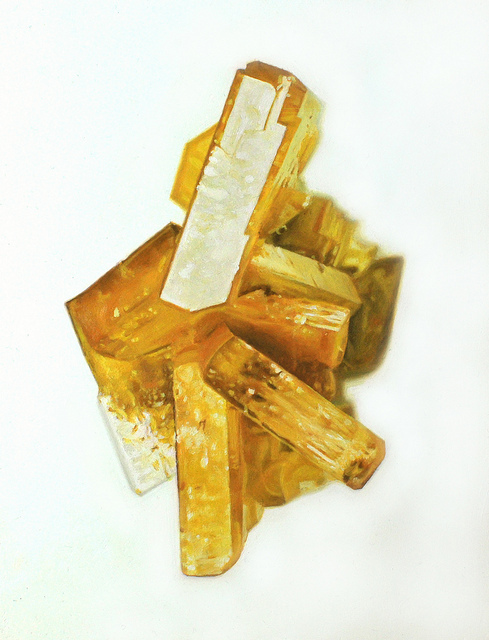
I am delving into dark currents, the scientific poetry of video. This is what mimesis seeks to screen out: the medium. Or more specifically, the primacy of the pheno-text. I would even call it the accountability of the image. The video image is imagined as immaterial, and yet the material itself is expressive — literally. As Roland Barthes put it, "The 'grain' is the body in the voice as it sings, the hand as it writes, the limb as it performs." (IMAGE/MUSIC/TEXT, p.188)
In physics and in electronic engineering, dark current is the relatively small electric current that flows through photosensitive devices such as a photomultiplier tube, photodiode, or charge-coupled device even when no photons are entering the device. It is referred to as reverse bias leakage current in non-optical devices and is present in all diodes. Physically, dark current is due to the random generation of electrons and holes within the depletion region of the device that are then swept by the high electric field.
The charge generation rate is related to specific crystallographic defects within the depletion region. Dark-current spectroscopy can be used to determine the defects present by monitoring the peaks in the dark current histogram's evolution with temperature.
Dark current is one of the main sources for noise in image sensors such as charge-coupled devices. The pattern of different dark currents can result in a fixed-pattern noise; dark frame subtraction can remove an estimate of the mean fixed pattern, but there still remains a temporal noise, because the dark current itself has a shot noise. (WIKIPEDIA)

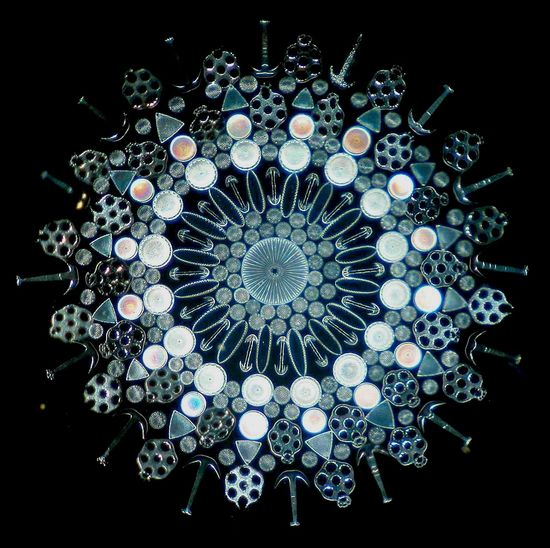 Arranged Exhibition Slide comprised of Diatoms, Sponge Spicules, and Plates and Anchors of Synapta; Imaged using Darkfield lighting technique.
Arranged Exhibition Slide comprised of Diatoms, Sponge Spicules, and Plates and Anchors of Synapta; Imaged using Darkfield lighting technique. Arranged mount of Sponge Spicula by A.C. Cole, imaged using Darkfield lighting.
Arranged mount of Sponge Spicula by A.C. Cole, imaged using Darkfield lighting. Arranged slide, Watson & Sons "Eggs of Butterflies, Etc." shown in detail.
Arranged slide, Watson & Sons "Eggs of Butterflies, Etc." shown in detail.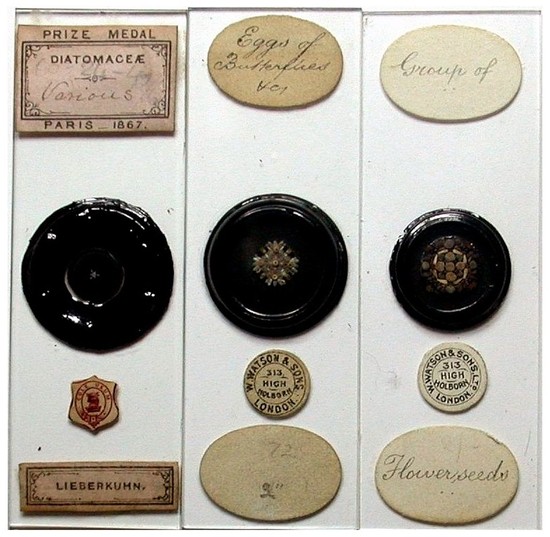 Three arranged slides on opaque backgrounds for incident lighting
Three arranged slides on opaque backgrounds for incident lighting



























